三代测序探索者每周文献精选
(08.22-08.28)
01
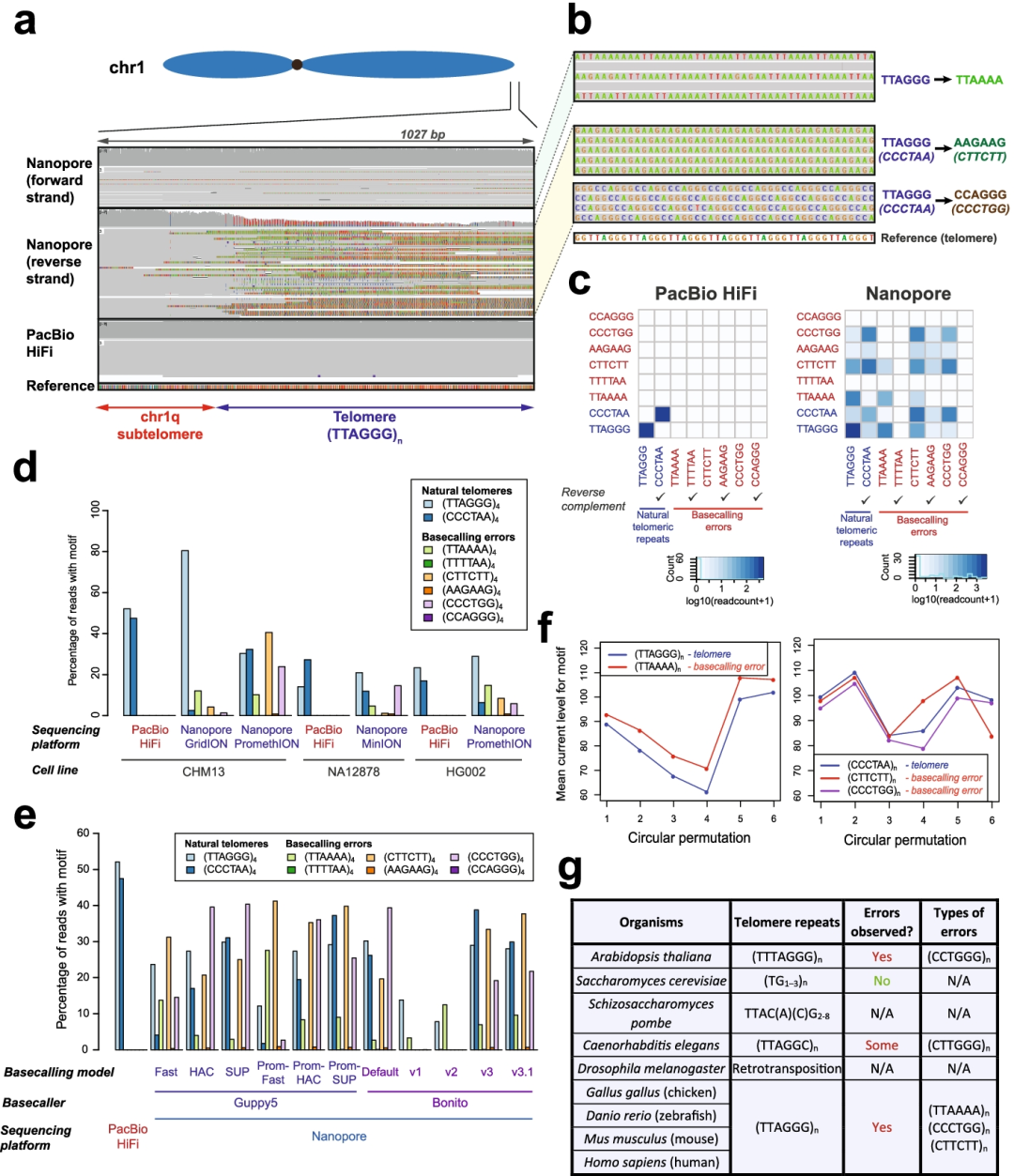
Fig1. Strand-specific nanopore basecalling errors are pervasive at telomeres.
亮点:作者在将nanopore序列比对到近测序和组装的人类基因组CHM13中的端粒区域进行分析时发现,基因组端粒区域经常以链特异性的方式被错误地标记为其他类型的重复。为了解决端粒上的这些碱基calling错误,作者通过提供更多的端粒训练示例来调整nanopore碱基calling程序。在训练数据上可以看到在端粒和亚端粒区域的basecalls准确性显著改善,并在染色体末端的错误明显减少。
02
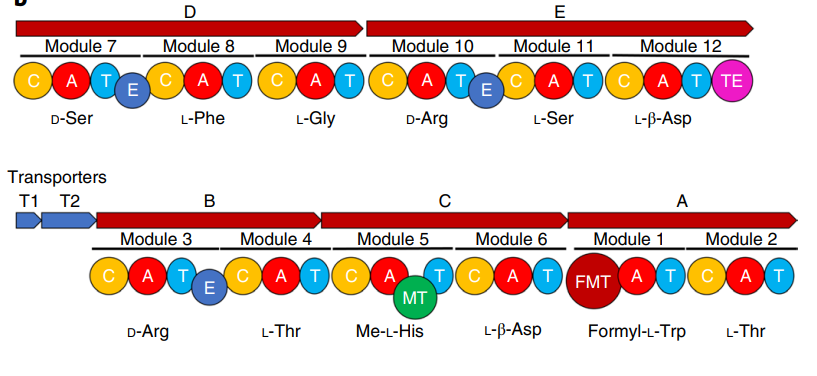
Fig2. The BGC of evybactin. Gene alignment of the BGC of evybactin in the producer strain. A–E are NRPS genes, and T1 and T2 are transporter genes.
亮点:The biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) of evybactin was determined using bioinformatic analysis of the genome. The genome was sequenced by a combination of Nanopore and Illumina reads (Microbial Genome Sequencing Center (MiGS)) and assembled into two contigs with a total size of 5.5megabases.The BGC of evybactin was identified as NRPS with a core BGC spanning 49.6 kilobases.
03
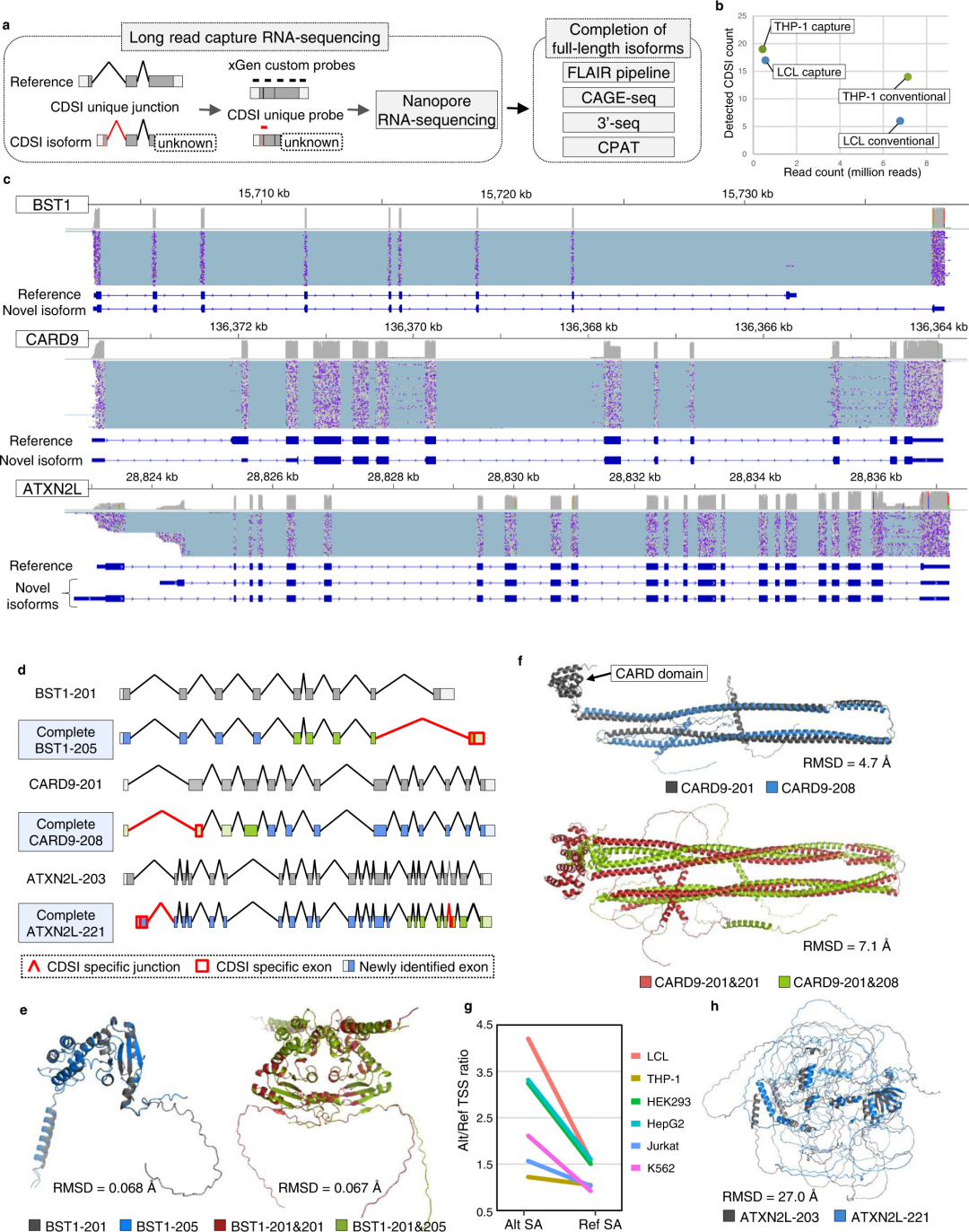
Fig3. Long-read capture RNA-sequencing for CDS incomplete isoforms.
亮点:We conducted long-read RNA-sequencing for the CDSI isoforms (37 isoforms in total), whose i-rQTL signals were co-localized with disease GWAS signals and whose unique splice junctions showed significant sQTL signals in LeafCutter analysis (FDR ≤ 0.05). The cDNAs were sequenced by MinION (Oxford Nanopore Technologies). We performed conventional long-read RNA-seq using 300 ng of total RNA from LCL and THP-1, then sequenced them using GridION X5 (Oxford Nanopore Technologies).
04
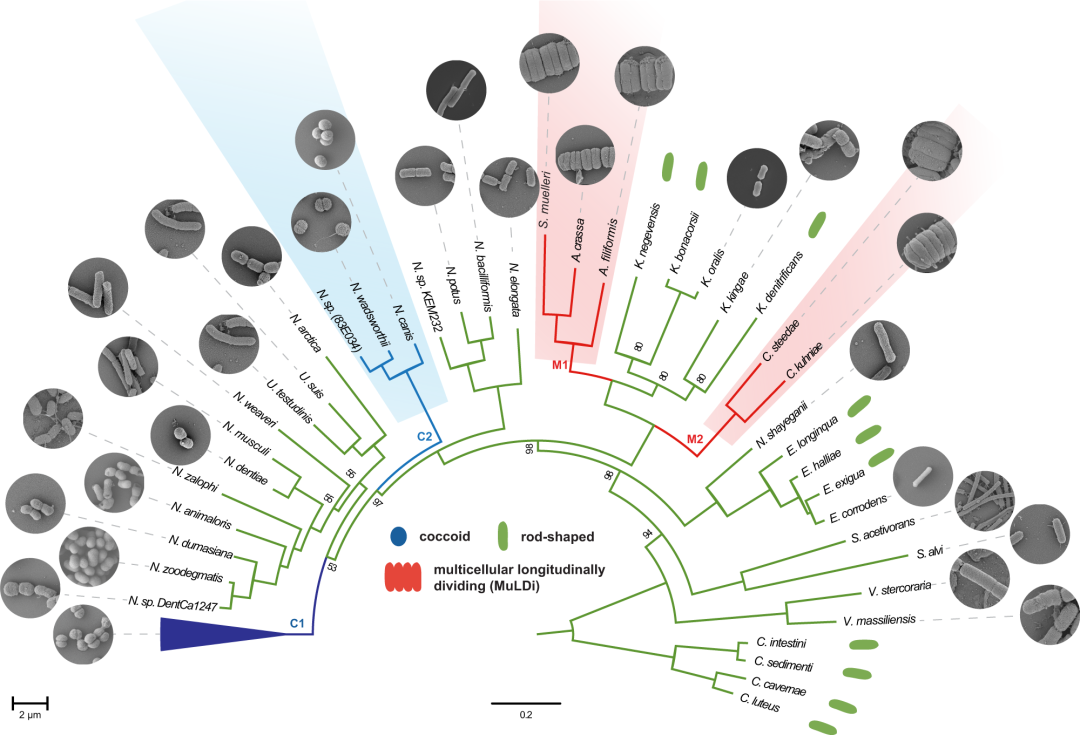
Fig4.Core genome-based phylogeny of rod-shaped, coccoid and MuLDi Neisseriaceae.
亮点: The Neisseriales order comprises the family Chromobacteriaceae and the family Neisseriaceae and more recently three additional families have been suggested, Aquaspirillaceae, Chitinibacteraceae and Leeiaceae. The family Neisseriaceae includes 12 genera . We selected species from each of these Neisseriaceae genera and used SMRT (PacBio) and Minion (Nanopore) technologies to obtain 21 closed genomes . Genomes obtained in this study were combined with Neisseriaceae draft genomes from the NCBI database to calculate the Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI). This enabled us to identify 75 Neisseriaceae species with genome ANI > 96%.
05

Fig5. Genomic characterization of Empoasca onukii and comparison with other insect genomes. A. Genomic characterization of the sequenced E. onukii. Track
亮点: In Asia, the tea green leafhopper (TGL), Empoasca onukii (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae), represents the most devastating pest across tea plantations, causing up to 50% economic loss of tea production annually. We generated a chromosome-level genome assembly of the E. onukii by integrating Illumina short reads, Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) long reads, and high-throughput chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C). This high-quality genome resource enabled us to investigate the genetic basis of chemoreception and detoxification in this insect, key to adapting to new environments.







